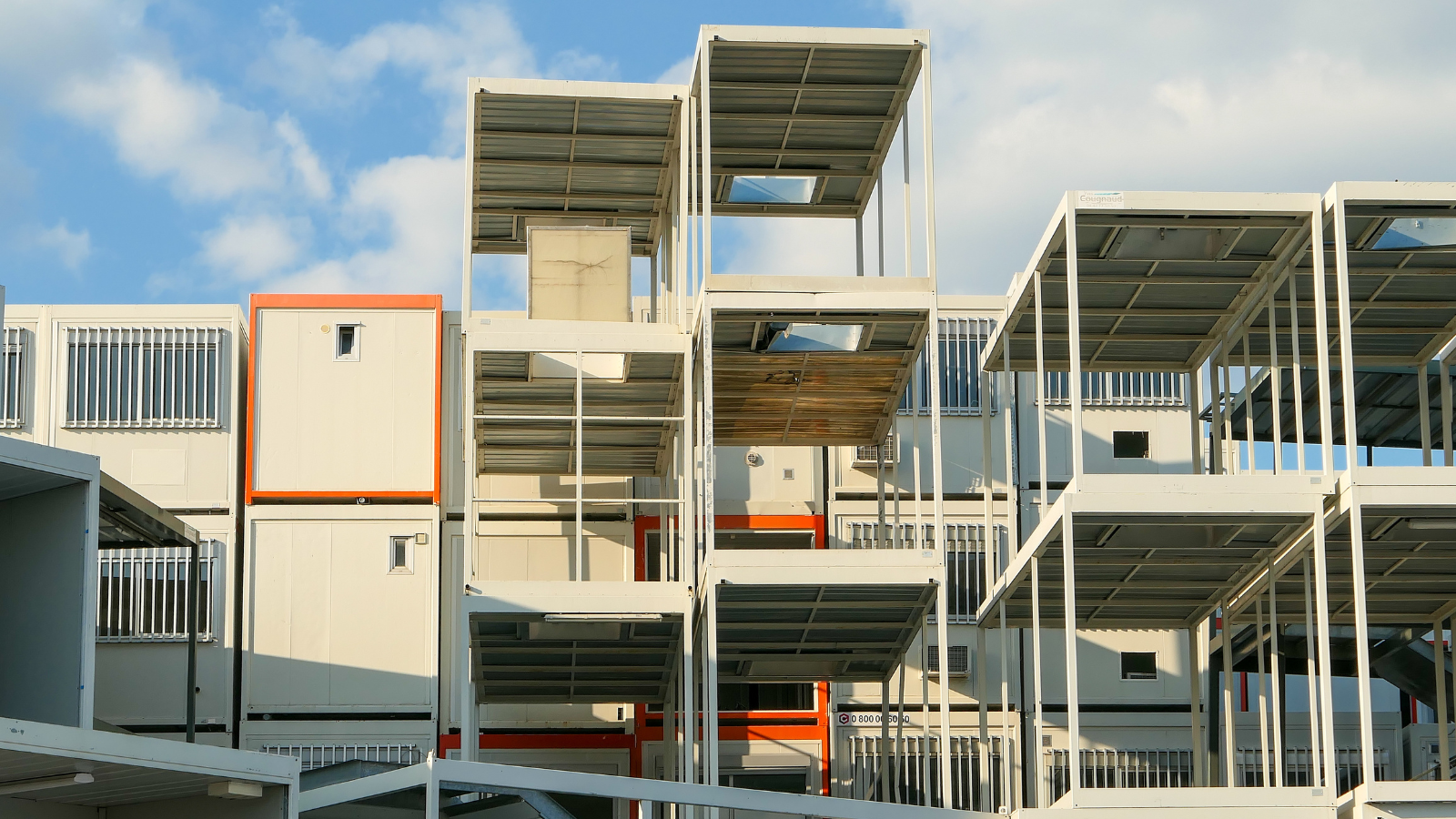
The construction industry is evolving rapidly, and one of the most significant transformations in recent years has been the rise of modular construction. With its focus on efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability, modular construction is reshaping how buildings are designed and erected. This method involves constructing mobile buildings or modular structures off-site in a controlled factory environment, then transporting and assembling them at the final site. The rise of modular construction offers numerous benefits, including faster build times, reduced costs, and lower environmental impacts, making it a key player in the future of sustainable building.
The Rise of Modular Buildings
In the face of increasing urbanisation, labour shortages, and rising construction costs, the building industry has been seeking more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable methods. Modular construction has emerged as a game-changer, offering solutions to these challenges. This innovative approach can be used for various building types, including homes, offices, hospitals, and even skyscrapers, providing flexibility and adaptability for projects of all sizes.
Modular construction provides benefits beyond just cost saving and efficiency. It is also a greener way to build, addressing the construction industry's responsibility for significant carbon emissions, waste, and energy consumption. As environmental concerns intensify, the ability to reduce both embodied and operational carbon emissions have made modular construction an increasingly attractive option.

Modular Structures: Biggest Benefits
- Faster Build Times: One of the most notable advantages of modular construction is speed. Unlike traditional construction, where building happens sequentially on-site, modular construction allows for the simultaneous construction of modules in a factory while site preparation occurs. According to NY Engineers, modular projects can be completed 30-50% faster than traditional methods, making it ideal for projects with tight timelines. Since much of the construction occurs in a controlled environment, weather delays are virtually eliminated, significantly speeding up the overall process.
- Reduced Material Waste: Traditional construction is notorious for its high levels of material waste, but modular construction offers a solution. Because materials are precisely measured and cut in a factory setting, there is far less waste compared to on-site construction, where excess materials often end up in landfills. This method also allows for better inventory control and recycling, further minimising environmental impacts.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Modular construction is inherently more cost-effective due to economies of scale. Large numbers of identical modules can be produced quickly in factories, cutting down on labour costs and minimising the likelihood of budget overruns due to delays or unforeseen issues. The controlled environment also reduces the risk of theft or damage to materials, leading to additional savings.
- Improved Quality Control: In traditional construction, the quality of work can vary significantly depending on external factors such as weather, labour skills, and site conditions. Modular construction, however, occurs in a controlled environment with strict quality checks at every stage. This approach results in buildings with fewer defects and greater overall durability.
- Sustainability and Reduced Carbon Emissions: Sustainability is a driving force behind the growing adoption of modular construction. Modular construction significantly reduces embodied carbon—the emissions associated with material extraction, processing, and construction. By minimising material waste and optimising energy use during manufacturing, modular buildings drastically reduce their carbon footprint.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Modular buildings offer flexibility that traditional construction methods cannot. They can be designed for permanent use or as relocatable buildings, allowing for easy adaptation to new sites or functions. This flexibility is especially valuable in rapidly changing urban environments, where buildings may need to be repurposed or relocated. In addition, modular construction's scalability makes it ideal for both small-scale residential projects and large commercial developments.
Modular Building Construction: Impactful Challenges
While modular construction offers numerous advantages such as faster build times, reduced costs, and improved sustainability, it is not without its challenges. These challenges arise from logistical, financial, regulatory, and perception-based obstacles that can hinder the full adoption of modular methods across the construction industry.
1. Transportation and Logistics
One of the primary challenges of modular construction is transporting prefabricated modules from the factory to the construction site. Modules can be large, heavy, and difficult to manoeuvre, especially when considering urban settings where roads may be narrow, or in rural areas where terrain is difficult to navigate. Moreover, these modules need to be carefully protected during transport to avoid damage, which adds to the logistical complexity. Coordinating the arrival of modules with on-site construction teams also requires precise scheduling to avoid costly delays. Transportation challenges not only increase costs but can also limit the size and design flexibility of modular components.
2. Regulatory and Zoning Restrictions
Local regulations and zoning laws can present significant hurdles for modular construction projects. Many areas have building codes designed for traditional construction methods, and these codes may not easily accommodate modular practices. In some cases, developers may face restrictions on the size, type, or number of modular buildings allowed in any given area. Furthermore, local authorities and planning departments may lack familiarity with modular construction techniques, leading to slower approval processes or additional scrutiny. For developers, navigating these regulations can result in delays and added costs.
3. Perception and Market Acceptance
Modular construction still suffers from some negative perceptions, particularly in residential markets. Many people associate modular buildings with low-quality or temporary structures, despite advances in technology that allow for high-quality, permanent modular constructions. Overcoming this stigma is crucial for the industry to gain widespread acceptance. Developers often need to invest in educating stakeholders—ranging from investors to potential tenants—on the durability, quality, and flexibility of modular buildings to change these outdated perceptions. There is still hesitation of investor interest.
4. Financial Challenges and Financing Models
Securing financing for modular construction projects can be more complex than for traditional builds. Lenders often view modular construction as riskier due to its relatively new and evolving nature, especially in markets where the practice is less established. This perception of risk can lead to higher interest rates or more stringent lending requirements. Additionally, modular projects are typically financed in two stages—construction and permanent occupancy—adding another layer of complexity to the process. Developers need to ensure that both stages of financing are adequately managed to prevent cash flow problems mid-project.
5. Workforce Adaptation
The modular construction process relies on a different skill set than traditional construction methods. Workers and project managers must adapt to new technologies and workflows, including factory-based manufacturing processes, advanced digital modelling tools, and more complex logistical planning. This learning curve can lead to initial inefficiencies and a period of adjustment for construction teams. Moreover, resistance to change among workers familiar with traditional methods can further slow the adoption of modular construction. Training programs and industry-wide standards will be essential to mitigate this challenge.
In conclusion, while modular construction offers innovative solutions to many challenges faced by the construction industry, it is still constrained by transportation logistics, regulatory hurdles, negative perceptions, financial complexities, and workforce adaptation. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for the modular industry to realise its full potential and become a mainstream construction method.
Modular Building Construction and Sustainability

Sustainability is one of the most significant advantages of modular construction, making it a key player in the movement towards greener building practices. As environmental concerns escalate globally, the construction industry has come under scrutiny for its substantial contribution to carbon emissions, resource depletion, and waste generation. Modular construction, with its controlled factory environment and efficient building practices, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional methods, addressing both embodied and operational carbon footprints.
1. Reduced Material Waste
One of the most critical sustainability benefits of modular construction is its ability to drastically reduce material waste. In traditional construction, materials are often over-ordered and cut on-site, leading to significant wastage. According to BuildingGreen, up to 30% of building materials used in traditional construction projects end up as waste. In contrast, modular construction takes place in a controlled environment where materials are precisely measured and cut, significantly reducing off-cuts and unused materials. Factory settings allow for better inventory management and the reuse of excess materials for future projects, further lowering waste.
2. Lower Embodied Carbon
The carbon footprint of a building is often measured in two forms: embodied carbon and operational carbon. Embodied carbon refers to the carbon emissions generated during the extraction, production, and transportation of building materials, as well as the construction process itself. Modular construction, by using prefabricated components produced in factories, optimises the use of materials and reduces the energy required to produce and transport them. Moreover, off-site manufacturing allows for greater use of sustainable and recyclable materials, which are often not feasible in traditional on-site builds.
3. Better Energy Efficiency
Modular buildings are inherently more energy-efficient due to their precise construction in a controlled environment. Factory-built modules are subject to rigorous quality control, ensuring better insulation, tighter seals, and less air leakage compared to site-built structures. These improvements reduce the energy required for heating and cooling, leading to lower operational carbon emissions throughout the building’s lifecycle. Additionally, modular construction is well-suited for integrating energy-efficient systems, such as high-efficiency HVAC units and renewable energy sources like solar panels, which further reduce the building’s environmental impact.
4. Improved Air Quality
Modular construction also contributes to sustainability by improving indoor air quality. Traditional construction often exposes materials to the elements, leading to moisture intrusion and the potential for mold growth. In contrast, modular buildings are constructed in climate-controlled factories, reducing the risk of moisture-related issues and enhancing indoor air quality. This controlled environment helps limit the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful emissions commonly associated with on-site construction materials, contributing to healthier living and working spaces for occupants.
5. Building Reusability
One of the most compelling sustainability features of modular construction is its alignment with the principles of the circular economy. Modular buildings are often designed to be disassembled and relocated, allowing for reuse of entire structures or individual modules in new locations. This approach extends the lifespan of buildings, reduces the need for new raw materials, and minimises waste. When a modular building reaches the end of its lifecycle, components can be refurbished or recycled, preventing them from ending up in landfills. This flexibility contrasts sharply with traditional buildings, which are often demolished when they are no longer in use, leading to significant waste generation.
In conclusion, modular construction offers a more sustainable approach to building by reducing waste, lowering carbon emissions, improving energy efficiency, and aligning with the circular economy. As the construction industry continues to grapple with its environmental impact, modular construction stands out as a viable solution that not only reduces the ecological footprint of buildings but also promotes long-term sustainability. With growing demand for green building practices, modular construction is poised to play a critical role in shaping a more sustainable future.
What’s Next for Modular Construction?

The future of modular construction looks promising as it aligns with several global trends, including the push for greener buildings and smarter cities. The integration of Building Information Modelling (BIM) and other advanced technologies is driving further innovation in the sector. BIM allows for precise design and planning, reducing the likelihood of errors during the construction phase and enabling greater collaboration between architects, engineers, and builders.
The demand for affordable housing, particularly in urban centres, is also fuelling the adoption of modular construction. Governments and developers are increasingly turning to modular methods to meet the rising demand for low-cost, sustainable housing. In cities like New York, where high construction costs have long been a barrier to affordable housing, modular construction is providing a viable solution.
Conclusion
Modular construction is revolutionising the building industry by offering faster, more cost-effective, and sustainable alternatives to traditional construction methods. Its ability to reduce waste, lower carbon emissions, and improve build quality makes it an attractive option for both developers and environmental advocates. As urbanisation continues to increase, and environmental concerns become more pressing, modular construction will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of sustainable building.
About us
Stonehaven is a trusted project management company and construction consultant based in Dubai, offering comprehensive construction management services across the UAE with offices located in Dubai, UK and Sri Lanka. As one of the leading project management companies in Dubai, we manage projects from inception to completion, ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness at every stage.
We deliver value through expert project management consultancy services, tailored to meet the unique needs of each client. Our core services include Cost Management, Project Management, Construction Supervision, Engineering Support, Design Support, and Marketing & Communications. Whether you’re looking for construction consultants or project managers in the UAE and wider GCC region, Stonehaven is your trusted partner for achieving excellence in your next project.
At Stonehaven, we are dedicated to supporting the next generation of building projects through innovative modular construction solutions. Our expert team works with clients to design and deliver high-quality, sustainable buildings that meet the challenges of today’s construction industry. Whether you're looking to develop affordable housing, commercial spaces, or bespoke residential projects, Stonehaven is your trusted partner in modular construction.
Contact us today to learn how we can help bring your vision to life while promoting sustainability and efficiency in every build.