The construction tender process plays a pivotal role in the success of any project, ensuring the selection of the most qualified contractors and suppliers while promoting transparency and cost-efficiency. For project owners, navigating the tender process effectively is not just about compliance—it’s about securing quality and ensuring timely delivery.
This guide dives deep into the construction tender process, offering a clear roadmap for project owners managing building construction tenders, tenders for construction work, or UAE construction tenders. We’ll also explore actionable insights, emerging trends, and strategies to overcome common challenges, ensuring your tenders stand out in today’s competitive environment.
What is the Tendering Process in Construction?
The construction tender process flow involves a structured series of steps designed to help project owners solicit bids, evaluate proposals, and award contracts to the most suitable contractor. This process ensures fairness, promotes competition, and aligns project goals with industry best practices.
Construction tenders are crucial for increasing the chances of securing lucrative projects, with $101 billion worth of projects awarded in the MENA region in the first half of 2023, 67% of which were in Saudi Arabia and the UAE. Well-prepared tenders align with client priorities, making them key in this competitive market.

The Steps in the Tendering Process:
- Pre-Tender Planning: Defining the project requirements and establishing timelines.
- Tender Document Preparation: Crafting comprehensive documents with specifications, terms, and evaluation criteria.
- Invitation to Tender (ITT): Advertising the tender or inviting specific contractors.
- Bid Submission: Contractors submit their proposals in response to the ITT.
- Bid Evaluation: Proposals are reviewed and shortlisted based on technical compliance, pricing, and timelines.
- Awarding the Contract: The winning bidder is selected, and the agreement is formalised through construction contract drafting.
Each of these steps requires proper attention to detail. Errors in any stage—be it unclear documentation or poorly defined evaluation criteria—can lead to costly disputes or project delays.
Why is the Tendering Process Important?
The tendering process is essential for project owners to:
- Secure Competitive Pricing: A transparent process ensures the best value for money against competitive prices.
- Ensure Compliance: Align with local regulations for UAE construction tenders or international standards such as FIDIC tender documents.
- Select the Right Expertise: Contractors are evaluated on their ability to deliver quality work within the defined scope and timeline.
By mastering the tendering process, project owners can set their projects up for success.
Tendering Process Steps in Construction: A Detailed Breakdown
To effectively navigate the tendering process steps in construction, it’s essential to break down each phase and understand its role in the overall project lifecycle. Here’s an expanded look at the process:
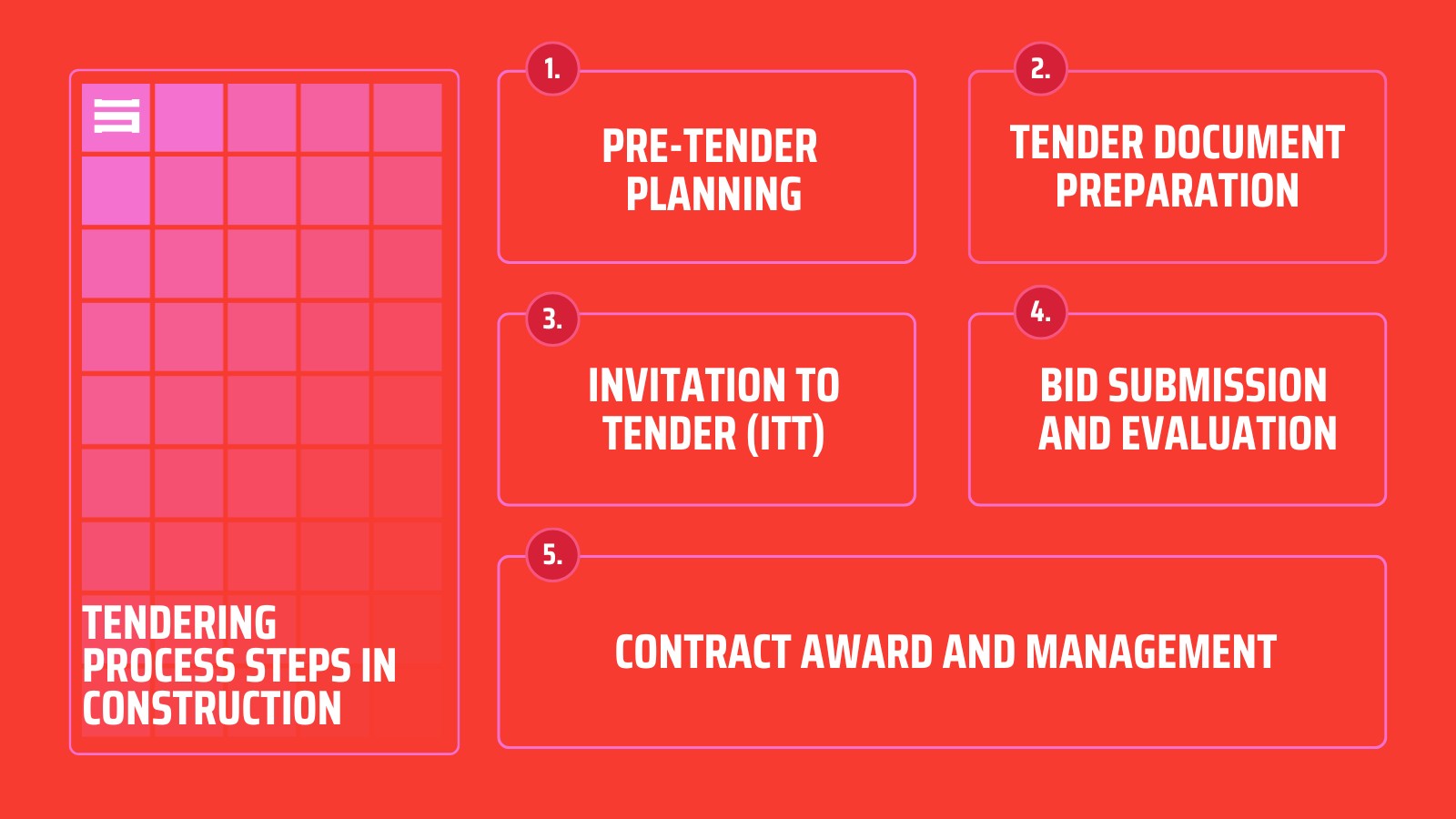
Step 1: Pre-Tender Planning
Before drafting tender documents, project owners must have a clear understanding of the project’s scope, objectives, and constraints. Key considerations include:
- Budget and Timeline: What are the financial and time constraints for the project?
- Regulatory Requirements: Are there specific local or international regulations that must be followed (e.g., UAE construction tender regulations)?
- Stakeholder Alignment: Have all stakeholders agreed on the project’s scope and priorities?
This stage sets the foundation for the tendering process. Poor planning at this stage can result in vague tender documents or misaligned expectations, leading to delays and disputes.
Step 2: Tender Document Preparation
Tender documents are the blueprint for the bidding process, outlining everything contractors need to know to submit a proposal. Critical components include:
- Scope of Work: Clearly defined tasks, deliverables, and expectations.
- Evaluation Criteria: Metrics for assessing contractor proposals (e.g., cost, quality, experience).
- Legal Terms: Including dispute resolution mechanisms and compliance requirements, often aligned with FIDIC tender documents.
- Submission Guidelines: Details on deadlines, formats, and required supporting documents.
Professional tender document preparation services ensure these documents are precise and aligned with industry norms.
Step 3: Invitation to Tender (ITT)
The ITT stage involves publishing the tender to attract bidders. Project owners can opt for:
- Open Tenders: Publicly advertised tenders that encourage competition.
- Selective Tenders: Invitation-only tenders for pre-qualified contractors.
- Private Tenders: Directly approaching specific contractors, commonly used for private company tenders.
Step 4: Bid Submission and Evaluation
Once contractors submit their bids, project owners must evaluate them based on:
- Technical Compliance: Does the contractor’s approach align with the project’s requirements?
- Cost: Is the pricing competitive while meeting quality expectations?
- Experience: Does the contractor have a proven track record of handling similar projects?
This stage may involve multiple rounds of evaluations, particularly for complex projects.
Step 5: Contract Award and Management
After selecting the winning bidder, the project enters the contract finalisation phase. A well-drafted agreement, created through construction contract drafting, ensures all parties are aligned on responsibilities, timelines, and risk management strategies.
Types of Tenders in Construction
Selecting the right type of tender is one of the most critical decisions a project owner makes. Each tender type serves a unique purpose and is suited to specific project requirements. Understanding these types allows project owners to align their goals, budget, and timeline with the most effective tendering strategy.
Below is a detailed explanation of the most common types of tenders used in the construction industry, along with their applications, advantages, and limitations.
1. Open Tenders
Definition: Open tenders are publicly advertised, allowing any qualified contractor to submit a bid. This is the most transparent and competitive tendering process.
Applications:
- Government projects requiring compliance with public procurement regulations.
- Infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and public buildings.
- Large-scale construction projects with significant budgets and timelines.
Advantages:
- Maximum Competition: Since the tender is open to all, it attracts a wide range of bidders, often resulting in competitive pricing.
- Transparency: Public advertisement and bidding ensure accountability and fairness, which is especially important for government tenders.
- Broader Options: Owners have access to a larger pool of contractors, increasing the chances of finding the most suitable bidder.
Limitations:
- Time-Consuming: Evaluating many bids can be resource intensive.
- Variable Quality: Open access means bids from less experienced or unqualified contractors may also need to be reviewed.
- Increased Administrative Burden: Managing multiple submissions and queries requires additional effort.
2. Selective Tenders
Definition: In selective tenders, only pre-qualified contractors are invited to bid. This process narrows the field to experienced contractors with proven expertise.
Applications:
- Private company tenders where quality and reliability are prioritised over cost alone.
- Projects requiring specialised skills, such as high-rise buildings or luxury residential developments.
- Situations where time constraints demand a streamlined process.
Advantages:
- Higher Quality Bids: Since contractors are pre-screened, bids are more likely to meet project requirements.
- Efficiency: The reduced number of bidders makes the evaluation process faster and more manageable.
- Targeted Expertise: Project owners can focus on contractors with relevant experience, reducing the risk of delays or substandard work.
Limitations:
- Limited Competition: Restricting the pool of bidders may reduce cost competitiveness.
- Potential Bias: If not managed transparently, selective tendering can lead to accusations of favouritism.
3. Negotiated Tenders
Definition: In a negotiated tender, the project owner negotiates directly with one or more contractors instead of inviting bids through a formal process. This method is often used for specialised projects or situations where time is a critical factor.
Applications:
- Projects requiring a specific contractor’s expertise, such as hospitals, laboratories, or bespoke architectural designs.
- Fast-track projects where starting construction quickly is essential.
- Extensions or modifications to existing projects where continuity is important.
Advantages:
- Collaboration: Direct negotiation fosters better communication and alignment between the project owner and contractor.
- Speed: Eliminates the lengthy bidding process, making it ideal for urgent projects.
- Customised Solutions: Allows for greater flexibility in pricing, timelines, and contract terms.
Limitations:
- Lack of Competition: Direct negotiation can result in higher costs due to the absence of competing bids.
- Reduced Transparency: Without a formal bidding process, there is less accountability, which can lead to disputes or mistrust.
4. Two-Stage Tenders
Definition: A two-stage tender involves appointing a contractor during the design phase to provide input and collaborate on the project, with pricing and other details finalised in the second stage.
Applications:
- Large, complex projects with evolving requirements, such as airports, stadiums, or mixed-use developments.
- Projects requiring contractor input during the design stage to improve constructability.
- Situations where budget constraints require phased planning.
Advantages:
- Collaboration During Design: Contractors provide valuable insights during the design phase by working with lead design consultants or architects, leading to more efficient and cost-effective solutions.
- Flexibility: This approach accommodates changes in scope, materials, or budget during the early stages.
- Reduced Risk of Disputes: Early contractor involvement ensures alignment on expectations and technical feasibility.
Limitations:
- Uncertain Final Costs: Pricing is not fixed during the initial stages, which can lead to budget overruns.
- Potential Delays: Collaboration during the design phase can extend timelines if not managed effectively.
How to Choose the Right Tender Type
Selecting the best tender type depends on several factors:
- Project Complexity: Complex projects often benefit from two-stage or negotiated tenders due to the need for flexibility and collaboration.
- Budget: Open tenders are ideal for cost-sensitive projects where competition can drive down prices.
- Timeline: For fast-track projects, negotiated tenders can save time by bypassing the formal bidding process.
- Quality Requirements: If quality and expertise are paramount, selective tenders ensure high standards are maintained.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Construction Tender Process
Challenges in the Tender Process
- Regulatory Complexity: Adhering to regional laws and international standards like FIDIC tender documents can be overwhelming, especially for UAE construction tenders.
- Ambiguities in Documentation: Vague or incomplete tender documents can lead to misunderstandings and disputes.
- Time Pressures: Tight deadlines for preparing and evaluating tenders can compromise thoroughness.
- Evaluating Bids Objectively: Ensuring a fair evaluation process requires clear criteria and impartiality.
Opportunities That Open in Tendering

By proactively addressing challenges and leveraging opportunities, project owners can enhance the success of their tenders.
What are the Tips for Enhancing Your Tendering Process?
- Leverage Technology: Tools like Procore streamline tender document preparation, submission tracking, and bid evaluation.
- Engage Experts: Professional tender document designers ensure clarity, compliance, and precision.
- Focus on Evaluation Criteria: Use transparent metrics to ensure a fair and unbiased evaluation process.
- Embrace Sustainability: Incorporate eco-friendly practices into your project scope to align with industry trends.
These tips help project owners optimise their tendering processes and achieve better outcomes.
Emerging Trends in the Construction Tender Process
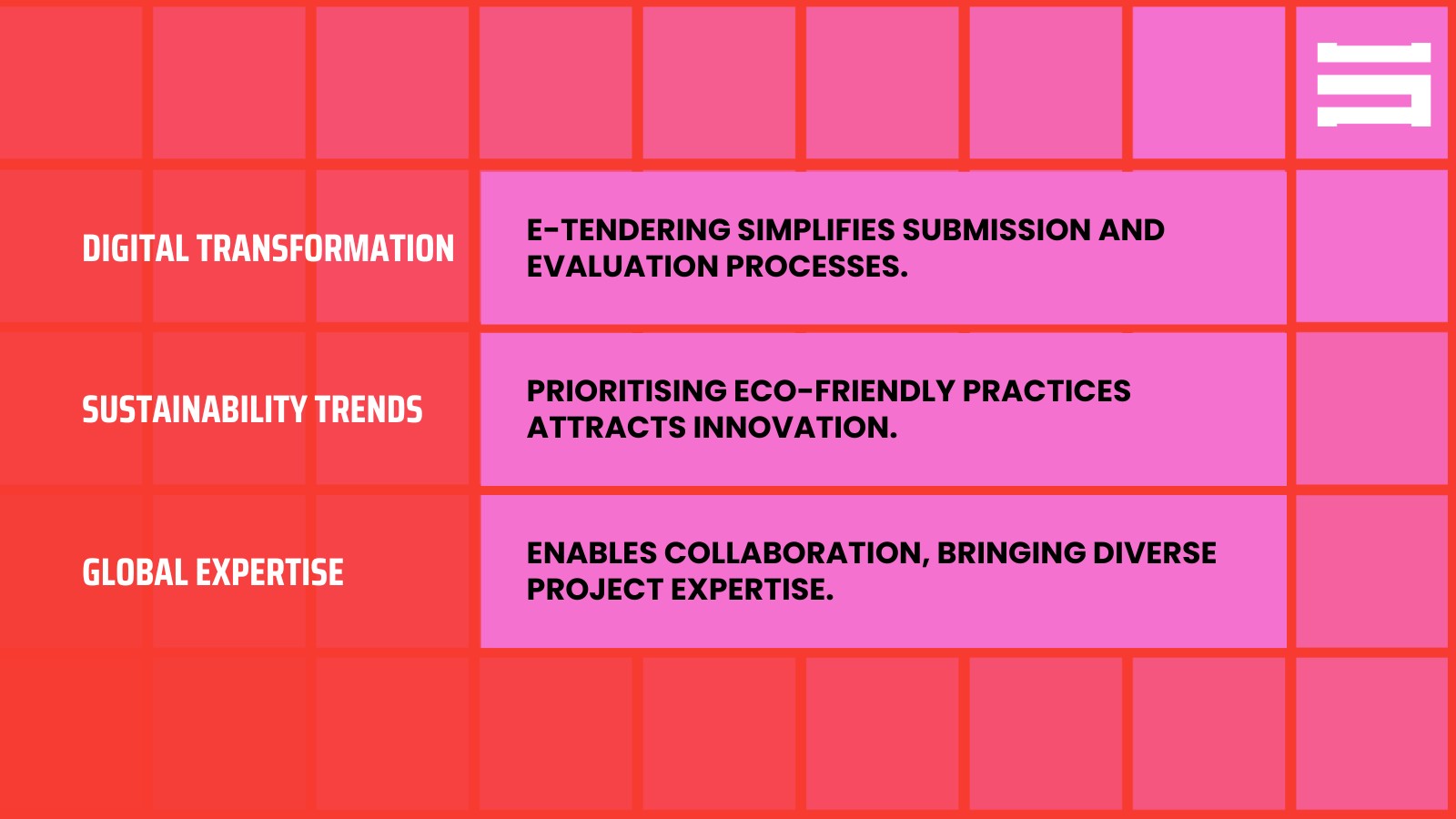
The construction industry is evolving rapidly, and the tendering process is no exception. Key trends include:
- BIM Integration: Building Information Modelling (BIM) enhances project transparency by providing detailed visualisations during the tender phase.
- AI-Driven Analysis: Artificial intelligence speeds up bid evaluations, improving objectivity and reducing errors.
- Digital Tendering Platforms: E-tendering systems automate repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing costs.
- Sustainability Metrics: With the rise of green building standards, tenders now need to prioritise eco-friendly practices.
Staying ahead of these trends ensures your tendering process remains competitive and effective.
Conclusion
The construction tender process is more than a procedural requirement—it’s a strategic tool for project success. By mastering the tendering process steps in construction, leveraging emerging technologies, and addressing challenges proactively, project owners can secure the best contractors and deliver projects efficiently.
Whether managing building construction tenders or exploring opportunities in UAE construction tenders, this guide equips you with the knowledge and strategies to excel.
About us
Stonehaven is a trusted project management company and construction consultant based in Dubai, offering comprehensive construction management services across the UAE with offices located in Dubai, UK and Sri Lanka. As one of the leading project management companies in Dubai, we manage projects from inception to completion, ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness at every stage.
We deliver value through expert project management consultancy services, tailored to meet the unique needs of each client. Our core services include Cost Management, Project Management, Construction Supervision, Engineering Support, Design Support, and Marketing & Communications. Whether you’re looking for construction consultants or project managers in the UAE and wider GCC region, Stonehaven is your trusted partner for achieving excellence in your next project.
At Stonehaven, we specialise in tender document preparation services and construction contract drafting. Whether you’re managing UAE construction tenders or private projects, we ensure precision, compliance, and excellence at every stage.
Let us simplify your tendering journey. Contact Stonehaven today and set your project up for success with our expert guidance tailored to your needs.