The construction industry is a dynamic landscape, where project success relies on precision, collaboration, and meeting client expectations. Among the myriad factors that contribute to a successful project, Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) stand as critical components. They ensure that every brick laid, and beam raised is in line with predetermined quality benchmarks, delivering results that are safe, durable, and aligned with client aspirations.
With increasing competition among construction project management companies, QA and QC have become more than compliance measures—they are tools for differentiation. For Stonehaven, QA/QC is a fundamental practice embedded in every phase of our project delivery. By proactively identifying and addressing risks, we ensure that quality is not just maintained but optimised in all our projects.
In this guide, we’ll unpack the essentials of QA/QC in construction, discuss their importance, explore practical approaches, and shed light on emerging trends. Whether you're a client, contractor, or consultant, understanding and implementing effective QA/QC systems can transform your projects and build lasting trust with stakeholders.
What is QA/QC in Construction?
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are two intertwined disciplines that govern the standards and quality of construction projects. Together, they establish a framework to manage risks, streamline processes, and deliver exceptional results.

Together, QA and QC create a holistic quality management system that balances prevention and correction. This not only enhances the final output but also builds trust, reduces costs, and ensures safety—cornerstones of any successful construction endeavour.
Approximately 74.2% of global construction markets are experiencing difficulties in finding skilled workers, leading to potential quality issues. Implementing comprehensive QA/QC protocols is quite vital to mitigate the risks associated with labour shortages and other vulnerabilities that can occur in the market.
How Construction Consultants Can Ensure Quality Assurance and Control
Construction consultants play a pivotal role in ensuring quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) throughout a project. Their responsibilities span from pre-construction planning to final project handover, focusing on maintaining high standards of safety, durability, and performance.
By adopting a structured and collaborative approach, consultants help mitigate risks, streamline processes, and achieve project success.
Responsibilities of Cost Managers and Project Managers in QA/QC
Material Inspections
- Approach: Cost managers ensure that procurement aligns with budgetary constraints without compromising quality, working closely with vendors to verify material compliance. Project managers oversee the inspection of materials upon delivery to the site, ensuring they meet design specifications and approved standards. Together, they coordinate the rejection or replacement of substandard materials while managing cost implications and project timelines.
- Example: For a large-scale commercial project, cost managers negotiate with suppliers to procure high-grade concrete within budget, while project managers ensure that each batch undergoes slump testing and compressive strength verification.
Process Monitoring
- Approach: Project managers conduct routine site inspections to monitor construction activities, ensuring adherence to approved procedures. Cost managers evaluate the financial impact of non-conformance and coordinate with stakeholders to prevent costly rework. Both parties work together to ensure milestones are met without sacrificing quality.
- Example: During the installation of structural steel, project managers verify alignment with design tolerances, while cost managers assess the financial impact of delays caused by rework due to initial misalignments.
Documentation
- Approach: Cost managers maintain detailed records of procurement, material costs, and quality-related expenses to ensure transparency and alignment with the project budget. Project managers oversee inspection reports, non-conformance records, and corrective action plans, ensuring accurate and accessible documentation for stakeholders.
- Example: In an infrastructure project, cost managers maintain a budget tracker that includes expenses for quality testing, while project managers utilise inspection logs to address client queries and regulatory requirements.
Collaboration
- Approach: Cost and project managers act as a liaison between contractors, design teams, and clients to address quality concerns. Project managers lead on-site quality meetings, ensuring technical compliance, while cost managers provide financial insights into proposed corrective actions to balance quality with cost-efficiency.
- Example: When a contractor proposes using an alternative material to reduce costs, cost managers evaluate the financial savings, and project managers assess whether the substitute meets quality standards and project requirements.
At Stonehaven, our cost managers and project managers are integral to the QA/QC in projects. Their combined expertise ensures a holistic approach to quality, balancing financial efficiency with technical excellence. By proactively managing quality assurance and control, they help deliver projects that exceed client expectations while remaining on time and within budget. Their oversight and efforts ensure that quality is never compromised, reinforcing our commitment to safety, durability, and performance.
What are QA/QC Procedures?
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) procedures in construction are systematic protocols aimed at ensuring that every phase of a project meets established quality standards. These procedures are critical for maintaining consistency, minimising risks, and achieving project success. By integrating QA/QC procedures into the construction process, teams can ensure that materials, workmanship, and processes align with design specifications and regulatory requirements.
What are the Common QA/QC Procedures in Construction Projects?
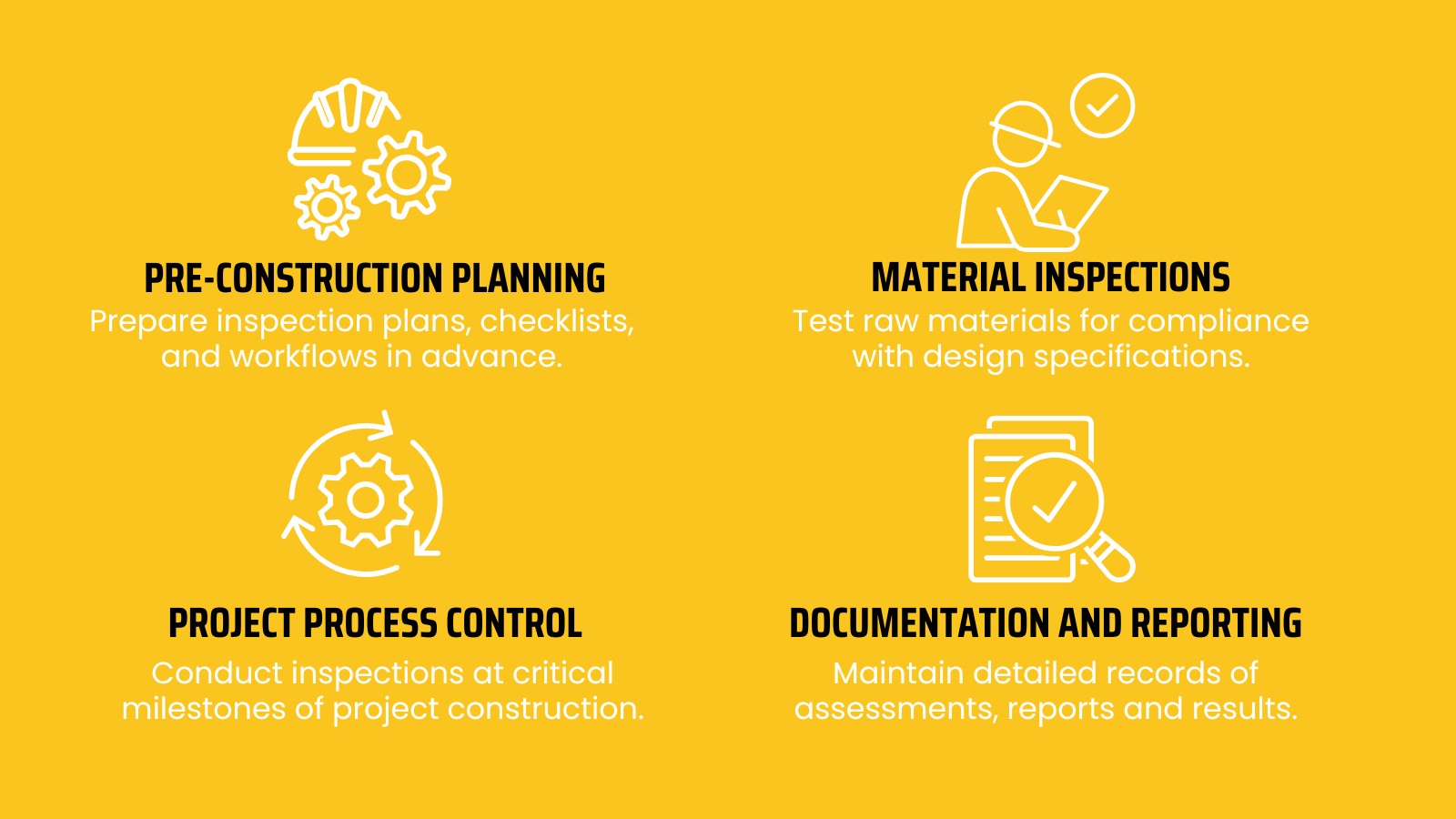
Pre-Construction Planning
- Scenario: A large-scale commercial project is about to begin, requiring clear quality benchmarks.
- Approach: During this phase, quality standards are collaboratively defined with stakeholders, ensuring alignment with client expectations and regulatory requirements. Detailed QA/QC documentation, such as inspection test plans (ITPs), checklists, and workflows, is prepared. Teams are trained on best practices to proactively prevent defects during execution.
- Outcome: Comprehensive planning reduces the likelihood of costly errors or delays, setting a strong foundation for quality assurance throughout the project.
Material Inspections
- Scenario: Concrete, steel, and other raw materials arrive at the site for use in structural work.
- Approach: Raw materials are tested to ensure compliance with design specifications, such as compressive strength for concrete or tensile properties for steel. Approved vendors and suppliers are pre-qualified based on quality benchmarks, ensuring reliable supply chains. Each batch is inspected upon arrival, and non-conforming materials are promptly rejected.
- Outcome: Thorough material inspections prevent substandard materials from compromising the safety and durability of the structure.
Project Process Control
- Scenario: The construction team begins installing critical structural components like beams and columns.
- Approach: Inspections are conducted at predefined milestones, such as foundation work, structural framing, and finishing stages. QC inspectors monitor workmanship to ensure it aligns with approved construction methods, identifying and correcting inconsistencies as they arise.
- Outcome: Process control ensures that every stage of construction meets quality standards, minimising defects and ensuring consistency in execution.
Documentation and Reporting
- Scenario: A client requests detailed updates on the quality status of an ongoing project.
- Approach: Detailed records of inspections, test results, and corrective actions are maintained in both physical and digital formats. Digital tools are utilised for real-time tracking, enabling seamless communication among stakeholders and fostering transparency. Comprehensive documentation ensures a clear audit trail and aids in resolving disputes if they arise.
- Outcome: Accurate reporting enhances stakeholder confidence and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
What is a QA/QC Checklist?
A QA/QC (Quality Assurance/Quality Control) checklist is a structured document that ensures all critical aspects of a construction project are inspected and verified according to predefined standards. It serves as a vital tool for maintaining quality and compliance, guiding QA/QC inspectors in systematically reviewing each phase of a project. By adhering to a checklist, inspectors can ensure that no critical element is overlooked, thus reducing the risk of errors, defects, or safety hazards.
Components of a QA/QC Checklist
A comprehensive QA/QC checklist typically includes the following components:
Material Checks
- Verifying that materials conform to the design specifications and meet project requirements.
- Inspecting the quality of materials upon delivery to ensure they are free from defects and suitable for use.
Workmanship Inspections
- Assessing construction methods to ensure compliance with approved standards, codes, and project specifications.
- Identifying and addressing inconsistencies or defects in execution to maintain structural integrity and quality.
Safety Protocols
- Confirming adherence to occupational health and safety guidelines, ensuring a safe working environment.
- Verifying that safety measures, such as protective equipment and emergency protocols, are in place and operational.
Documentation
- Reviewing and ensuring accuracy in records of inspections, test results, corrective actions, and compliance reports.
- Maintaining proper documentation to support accountability and streamline future audits.
What is a Quality Control Standard Operating Procedure (QC SOP)?
A Quality Control Standard Operating Procedure (QC SOP) is a formal document that outlines a systematic process for maintaining and verifying quality in construction projects. By standardising quality control practices, a QC SOP ensures consistent adherence to established standards, minimising errors, defects, and the need for rework. It serves as a comprehensive guide for project teams, ensuring that quality benchmarks are met at every stage of the construction process.
Key Elements of a Project QC SOP with Scenarios and Approaches
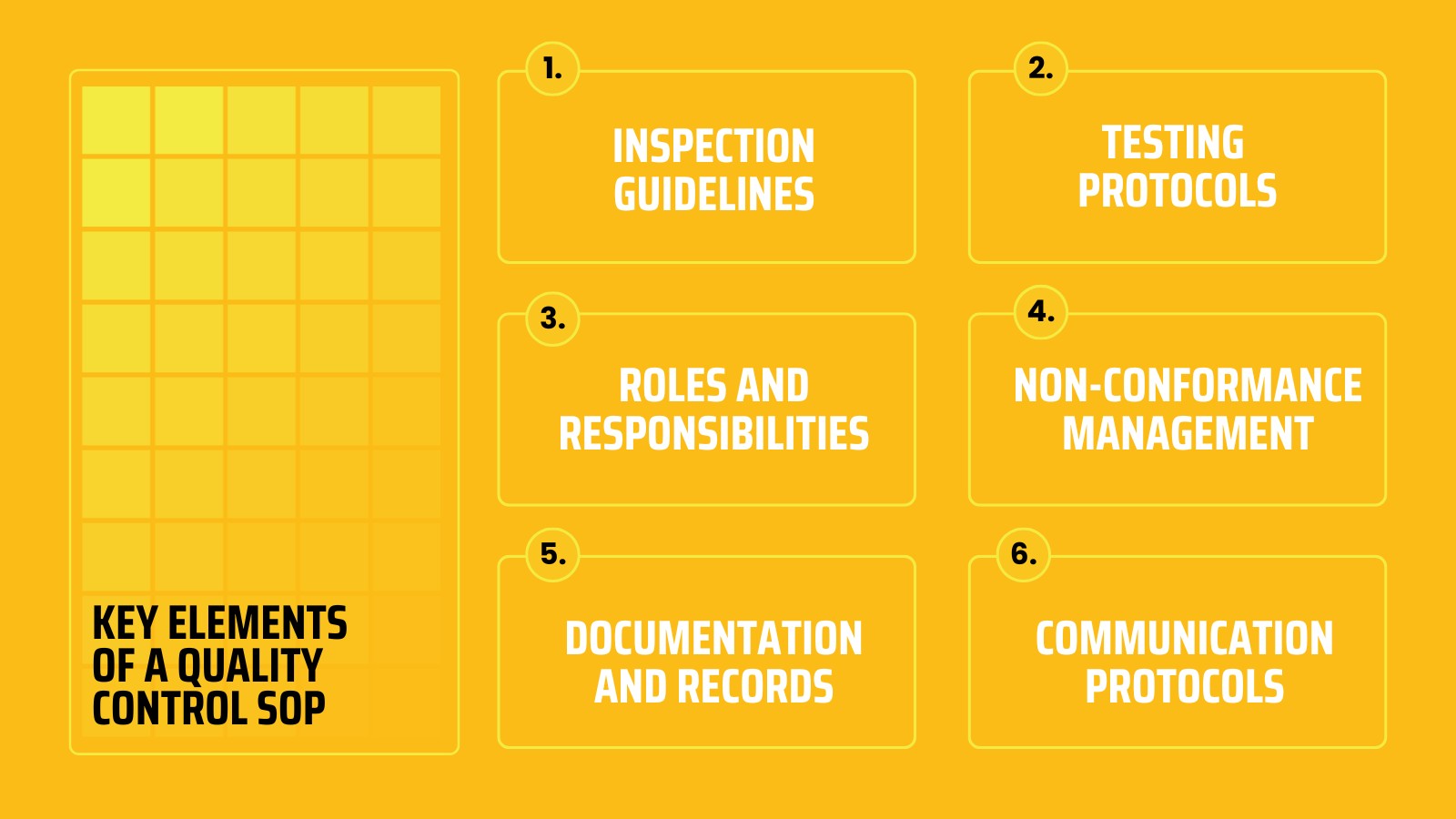
1. Inspection Guidelines
- Scenario: A batch of concrete is delivered to the site for casting a foundation. The quality of the material needs to be verified before use.
- Approach: Inspection guidelines specify the criteria for evaluating concrete quality. The QC team verifies the mix design against approved specifications and conducts on-site slump tests to assess workability. Random samples are taken for compressive strength testing in a laboratory. Inspections are also conducted during batching, delivery, and placement to ensure consistent compliance.
- Outcome: This approach helps identify potential quality issues, such as incorrect mix ratios, early on, thereby preventing structural failures.
2. Testing Protocols
- Scenario: Steel reinforcement bars are delivered to the site for structural elements.
- Approach: Testing protocols ensure the steel’s mechanical properties meet the project’s design specifications. Samples are tested in a certified laboratory for tensile strength and elongation, while visual inspections are carried out to check for rust, deformation, and mill markings. Any batch failing the required criteria is rejected and replaced.
- Outcome: Following these protocols ensures only materials meeting the project’s safety and quality standards are used.
3. Roles and Responsibilities
- Scenario: A defect in the plasterwork is identified during a routine inspection.
- Approach: The QC SOP clearly defines responsibilities. The site supervisor documents the defect and informs the QC officer, who investigates the root cause. The contractor responsible for the work is notified and asked to rectify the issue under the supervision of the QC team. If unresolved, the matter is escalated to the project manager.
- Outcome: Clear role allocation ensures swift action, minimising delays and maintaining project quality.
4. Non-Conformance Management
- Scenario: The alignment of a newly constructed wall deviates from the approved design.
- Approach: The QC SOP dictates a structured response. A non-conformance report (NCR) is issued, supported by photographic evidence and measurements. The contractor is instructed to correct the defect within a specified timeframe, with a follow-up inspection scheduled. Persistent issues may incur penalties, as outlined in the contract.
- Outcome: This systematic approach ensures defects are resolved efficiently, maintaining the quality and integrity of the project.
5. Documentation and Records
- Scenario: A client requests a quality control report during a progress review.
- Approach: The QC SOP ensures that all inspections, test results, and corrective actions are recorded systematically. Digital documentation, supported by photographs and detailed logs, is maintained in project management software for easy retrieval.
- Outcome: Well-organised records improve transparency, facilitate audits, and safeguard against disputes.
6. Communication Protocols
- Scenario: A subcontractor installs unapproved materials without informing the site team.
- Approach: Communication protocols ensure quality concerns are addressed promptly. Daily site meetings include updates on inspections and material approvals, while any deviations must be reported immediately. QC teams issue real-time updates to stakeholders via shared platforms.
- Outcome: Effective communication prevents misunderstandings, ensuring consistent compliance with quality standards.
Conclusion
Quality is at the heart of every successful construction project. Implementing robust QA/QC systems ensures that structures are safe, durable, and aligned with client expectations. By proactively managing quality through QA and addressing non-conformities with QC, construction firms can mitigate risks, reduce costs, and build lasting trust with stakeholders.
About us
At Stonehaven, quality is more than a promise—it’s a commitment. As a leading construction project management company, we specialise in providing end-to-end solutions that prioritise quality assurance and quality control in every phase of construction. From initial planning to final delivery, we work closely with our clients to ensure that every detail aligns with their vision.
With extensive experience working on projects across the UAE and beyond, we’ve earned a reputation as a trusted partner among construction project management companies in Dubai. Our expertise spans QA/QC planning, cost management, and leveraging advanced technologies to achieve the highest standards.
Partner with us to bring your construction vision to life. Trust Stonehaven to deliver results that stand the test of time. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how we can add value to your journey.